N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is a modified base which is abundant in mRNA in most eukaryotes but also has been found in tRNA’s, rRNA’s, snRNA’s and in long non-coding RNA’s. Adenosine methylation is catalyzed by m6A methyltransferase, a large protein complex which has a preference for the consensus sequence GGACU. In human, the m6A modification has been identified in more than 7000 genes. It is preferably present around stop codons and in the 3’ UTR but has not been observed in poly A tails. m6A is dynamically regulated both throughout development and in response to cellular stimuli. Levels are significantly higher in adulthood than during embryonic development. Although the presence of m6A in RNA was identified several years ago, it’s physiological significance remains largely unknown. It has been proposed to affect mRNA processing and export from nucleus to cytoplasm. Recently, it was shown that mutations in the m6A demethylase gene FTO, which cause a decrease of m6A levels, are associated with an increased risk for obesity and type 2 diabetes.
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) Antibody - RIP Grade
| Lot | 001 |
|---|---|
| Concentration | 2 μg/μl |
| Species reactivity | Human, mouse, other (wide range) |
| Type | Monoclonal |
| Purity | Protein A purified monoclonal antibody. |
| Host | Mouse |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C; for long storage, store at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage Buffer | PBS containing 0.05% azide. |
| Precautions | This product is for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Applications | Suggested dilution | References |
|---|---|---|
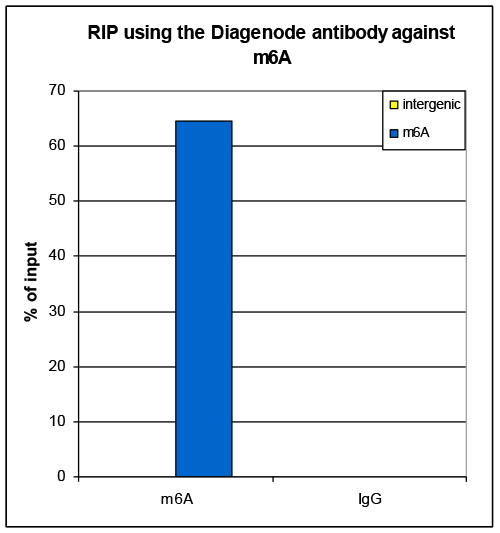
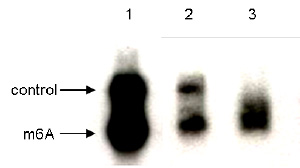
| RIP* | 2 µg per IP | Fig 1, 2 |
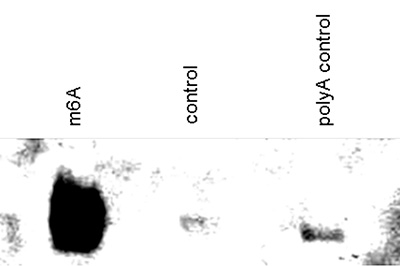
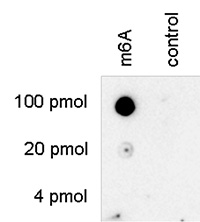
| Dot Blotting | 1:500 | Fig 3, 4 |
* Please note that the optimal antibody amount per IP should be determined by the end-user. We recommend testing 1-10 µg per IP.